Filing corporate taxes in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is straightforward, but understanding the basics is crucial for smooth compliance. As a business operating in the UAE, navigating the tax landscape effectively is essential. The UAE follows a territorial tax system, meaning companies are taxed on income generated within the country’s borders.
The UAE’s Federal Tax Authority (FTA) is the governing body overseeing tax matters, and companies are required to submit their annual tax returns to the FTA. This article will guide you through the fundamental steps of how to file for corporate tax in UAE, ensuring that your business meets its tax obligations accurately and efficiently.
Why it matters: Income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements form the base for tax filings.
Purpose: Tax authorities use these records to verify your reported income and expenses.
Why it matters: Illustrates adjustments impacting taxable income.
Purpose: Helps tax authorities understand changes made by businesses for accurate taxation.
Why it matters: Details of depreciation methods and calculations for assets.
Purpose: Affects taxable income; authorities use it to determine allowable depreciation deductions.
Why it matters: Crucial for cross-border businesses dealing with related entities.
Purpose: Ensures fair transactions; prevents manipulation to minimize tax liabilities.
Why it matters: Deals with transparency in transactions with relatives or related parties.
Purpose: Assesses fair dealings, avoiding preferential treatment.
Why it matters: Tracks changes in estimated liabilities or expenses.
Purpose: Ensures accurate reflection in financial statements and evaluates impact on taxable income.

Whether in a free zone or not, everyone subject to taxes must register for Corporate Tax and obtain a Corporate Tax Registration Number. For tax payments:
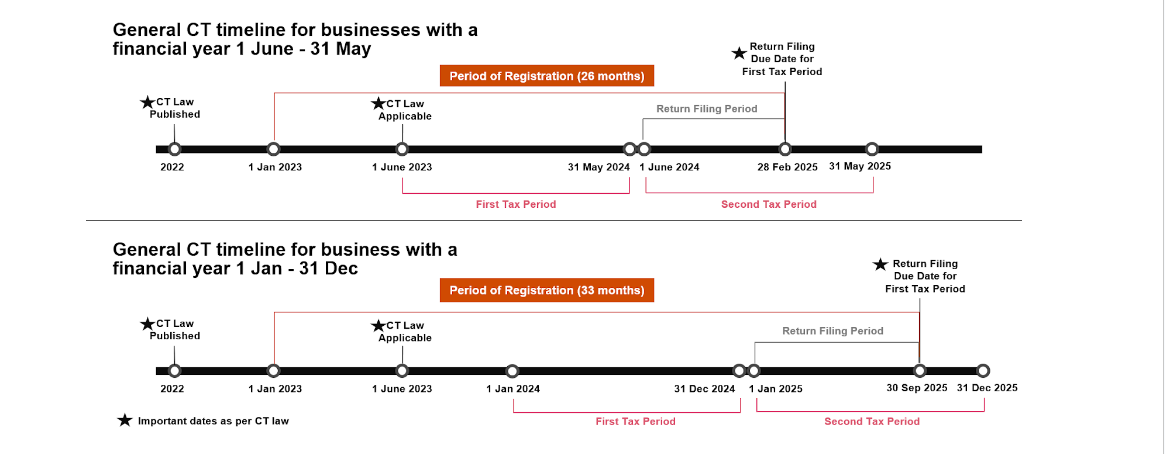
Illustrated below are examples of the registration, filing, and payment deadlines associated with Taxable Persons with a Tax Period (Financial Year) ending on 31 May or 31 December.
Two or more taxable persons may elect to form a tax group, allowing them to be treated as a single taxable person for corporate tax purposes. To qualify as a tax group, the following conditions must be met:
To determine the Taxable Income of a Tax Group, the parent company must prepare consolidated financial accounts covering each subsidiary that is a member of the Tax Group for the relevant Tax Period.
Transactions between the parent company and each group member and transactions between the group members would be eliminated for the purposes of calculating the Taxable Income of the Tax Group.
In the case of a tax group, the taxable income is calculated by preparing consolidated financial statements for the entire group. This means combining the financial statements of the parent company and all its subsidiaries into a single set of statements.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how to figure out the taxable income for a tax group:
This process can be complex and requires accounting and UAE corporate tax law expertise. It’s recommended to seek professional guidance from an accountant or tax advisor familiar with UAE corporate tax regulations to ensure accurate calculation and compliance.
Successfully filing corporate taxes in the UAE is a matter of systematic preparation and staying well-informed. By grasping the legal requirements, meeting deadlines, and fulfilling obligations mandated by the law, your business can confidently navigate the complexities of UAE corporate tax law.
As you approach the annual tax deadline, proactively address any queries or concerns promptly. With a diligent and informed approach, your business can efficiently fulfill its corporate tax obligations and contribute to its long-term financial success.